Chrome App Bound encryption
Chrome 127 introduces the concept of "App-Bound Encryption", which aims to make the job of stealing cookies harder.
You can read more about it here:
- https://security.googleblog.com/2024/07/improving-security-of-chrome-cookies-on.html
Data Format¶
Looks like the master key itself is the thing that's encrypted with the "App Bound" encryption.
So if we decrypt this then cookies are still portable as they were before.
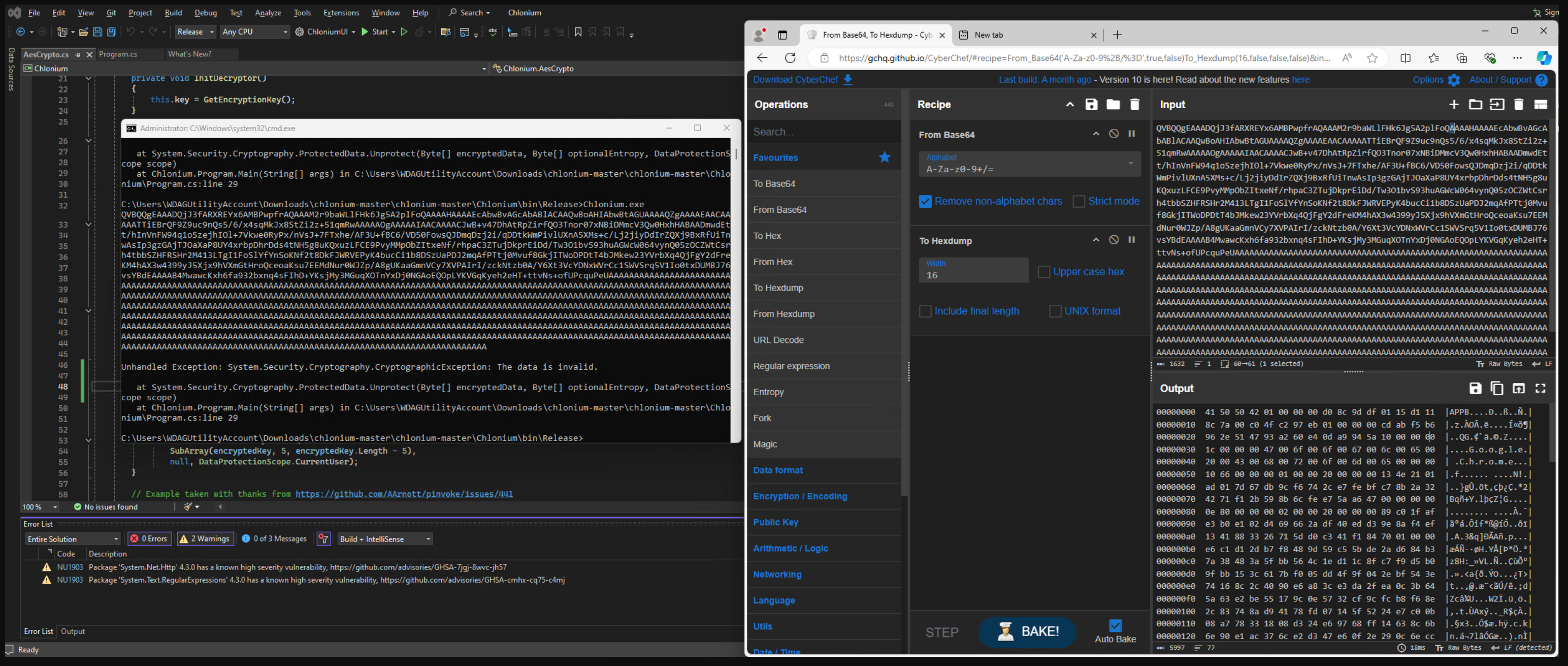
We'd need to convert this to a non app-bound key and then import into a fresh chrome with app-bound disabled, or dump the app bound key on a machine we control and then re-encrypt each item with our machine's app bound key (which is one of the import methods that Chlonium supports).
Disabling App Bound Encryption¶
There seems to be a number of ways to make Chrome fall back to the old behaviour (i.e. no App Bound encryption).
Network Directory Symlink¶
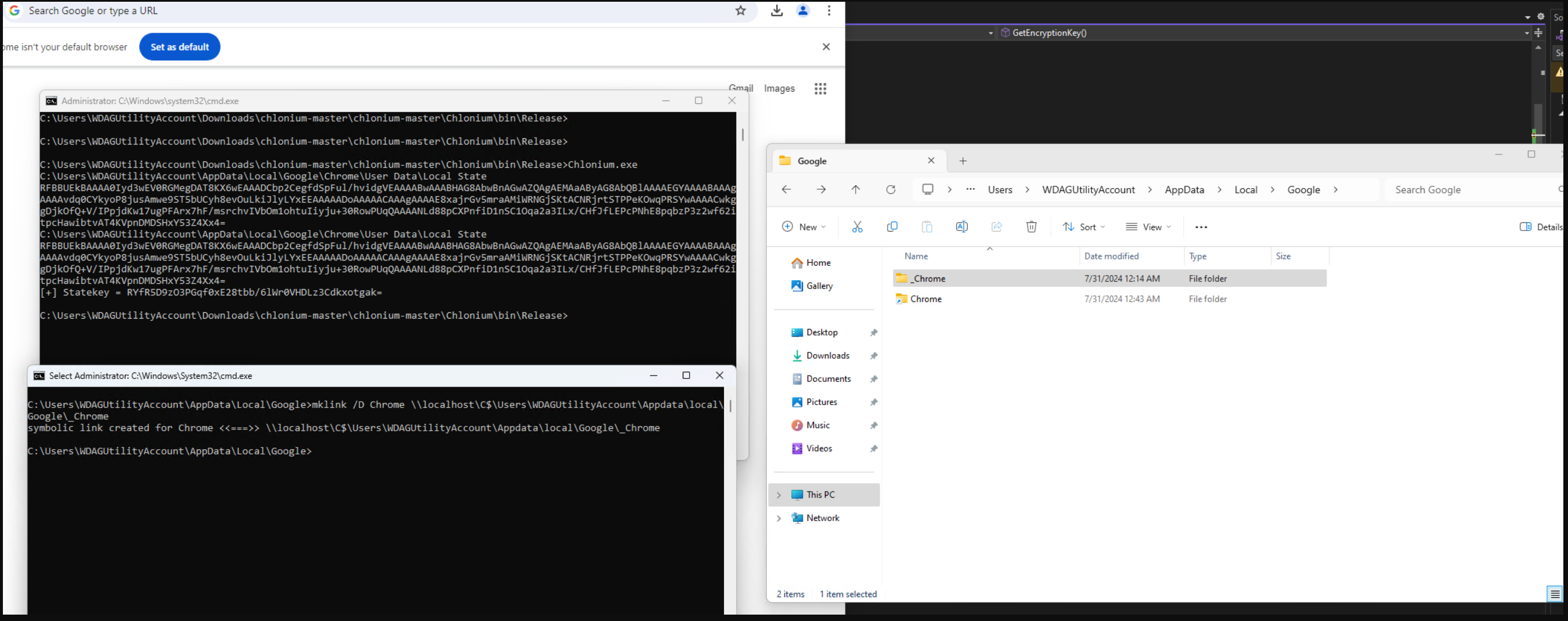
Make the Chrome folder a symlink to a network share on localhost. Chrome will then refuse to use App Bound encryption since it thinks the directory might be on a share and thus not be bound to a specific machine. As a result it falls back to the old DPAPI encryption.
Example:
The source can be seen in:
https://source.chromium.org/chromium/chromium/src/+/main:chrome/browser/os_crypt/app_bound_encryption_win.cc;l=74?q=APPB%20DPAPI&ss=chromium
IsNetwork just checks that the second character of the path is a path separator character (e.g. \), which it would be if it was a network share, e.g. \\localhost\c$
You can also modify the user data dir using command line flags but this can be seen by EDR easily:
You could also modify the %LOCALAPPDATA% environment variable for the Chrome process, either globally for the user via the registry, or by modifying the LNK file.
Override Setting¶
There is a setting which controls the flag g_non_standard_user_data_dir_supported_for_testing.
https://source.chromium.org/chromium/chromium/src/+/main:chrome/browser/os_crypt/app_bound_encryption_win.cc;drc=105770df485ace262780d95126bb60b1a16ec340;l=31?q=APPB%20DPAPI&ss=chromium
This is apparently set by policy (registry key), or via a command line option.
- There's a pref called
sync.enable_local_sync_backendwhich disables APPB if set totrue, because its detected as a Roaming Profile. - There's also a call to
GetProfileTypeto check if its set toPT_ROAMINGorPT_ROAMING_PREEXISTING. - There's a enterprise policy setting called ApplicationBoundEncryptionEnabled, which can disable APPB.
This sets the registry key:
Software\Policies\Google\Chrome\ApplicationBoundEncryptionEnabled
Which will be 0 (DWORD) for disabled.
- You can also set the
os_crypt.app_bound_encrypted_keypref in the Local State file.
Not Default Data Directory¶
Simply moving the user data dir to a non-default location also disables the feature. I'm not sure how this is set currently (need to check).
Chrome Process Path¶
If the Chrome process path does not start with \\Device\\HarddiskVolume, it falls back to the old behaviour.
Decryption¶
Data is decrypted using the elevator service which calls DecryptData via the IElevator COM interface.
https://source.chromium.org/chromium/chromium/src/+/main:chrome/browser/os_crypt/app_bound_encryption_win.cc;l=173;drc=105770df485ace262780d95126bb60b1a16ec340;bpv=0;bpt=1
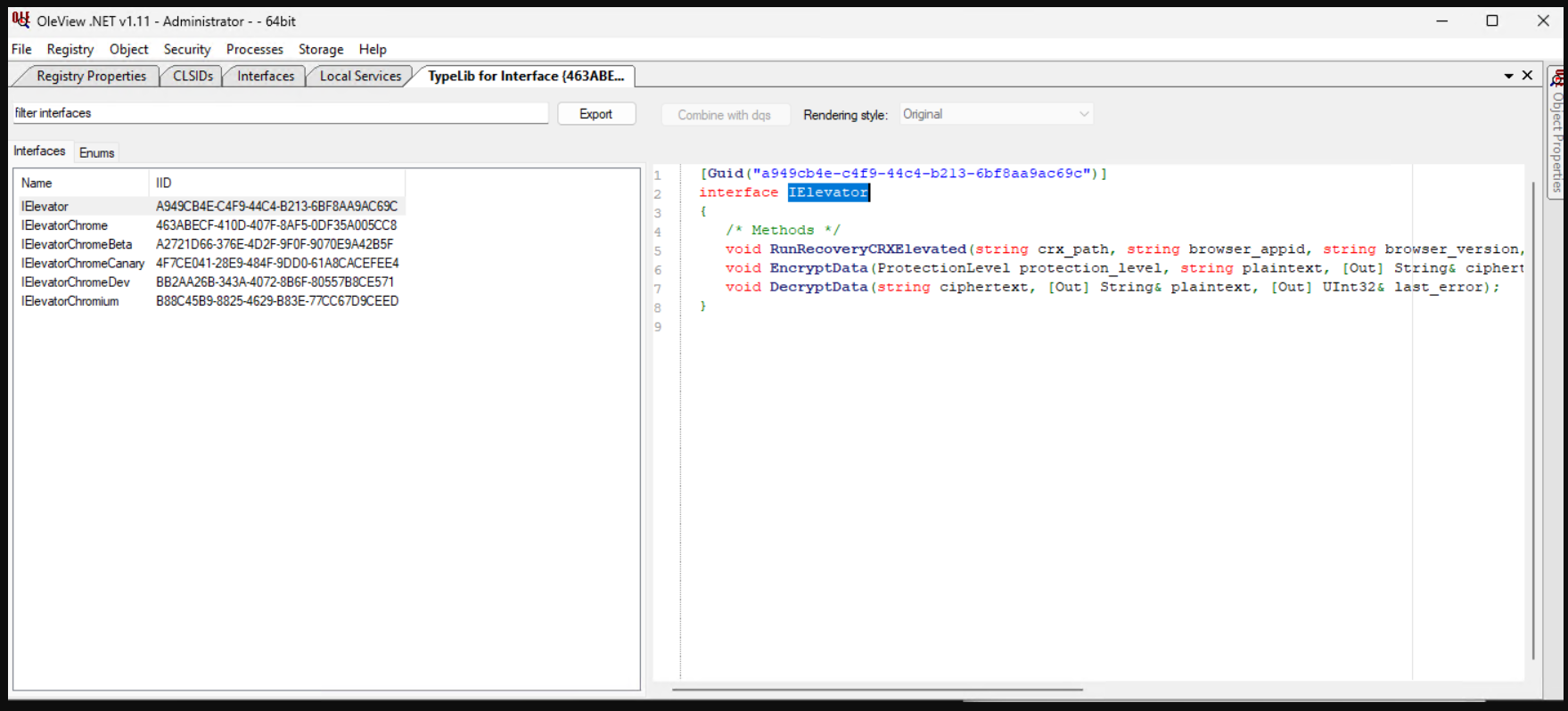
README for service¶
https://source.chromium.org/chromium/chromium/src/+/main:chrome/browser/os_crypt/README.md?q=appbound&ss=chromium%2Fchromium%2Fsrc&start=11
Decryption with Admin¶
This section details how you can decrypt cookies for import with Chlonium, when you have administrator access to the machine.
First you need to get the SYSTEM DPAPI key which you can get from the LSA secrets (using your favourite method).
Just for an example, with mimikatz this would just be:
or if you have a registry dump:
This can also be done remotely when you have admin using a tool such as SharpSecretsDump. However it cannot be done with a Domain Backup key, since the SYSTEM DPAPI master key is not protected with a Domain Backup Key.
Now look for a line like the following, which contains the DPAPI key:
With this key you can decrypt the SYSTEM DPAPI master key. But first we need to know which one to decrypt. For this we can try to first decrypt the App Bound key, which is stored in the Local State file.
You will find this at:
Open the file and look for a JSON value named app_bound_encrypted_key.
Copy out the value here as this is the SYSTEM DPAPI encrypted App Bound key which we need to decrypt with mimikatz.
Decode it from base64 to a file named app.bin.
Now open up mimikatz again and run:
Look for a line like this:
This indicates the SYSTEM DPAPI masterkey that we need to go and decrypt.
You will find this masterkey file in:
Now you can decrypt the SYSTEM masterkey with the following mimikatz command:
This should decrypt the SYSTEM key into your cache.
Now you can decrypt the App Bound key by running the same command as earlier but with the /unprotect flag:
If all goes well you should see some output like:
This is the decrypted DPAPI blob that you will be able to decrypt using your current user's DPAPI masterkey.
Save the data to a file named dpapi.bin (or run the command above again with the /out flag).
Now we run dpapi::blob again on the decrypted App Bound key:
Now it should decrypt the final key and you will see output like:
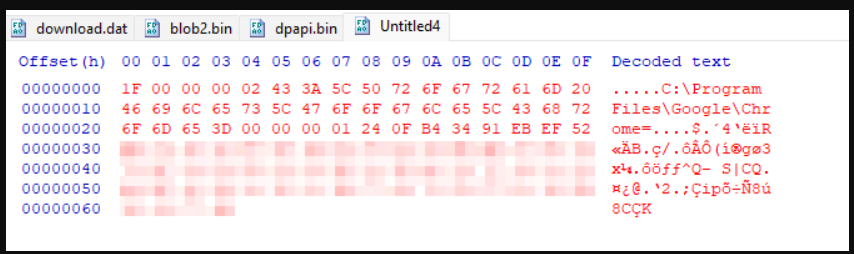
Save this to a file, as this contains the AES key we need to decrypt cookies! 🥳
It should look something like this, which seems to contain a path (for the App-Bound process identity?), and an AES key: